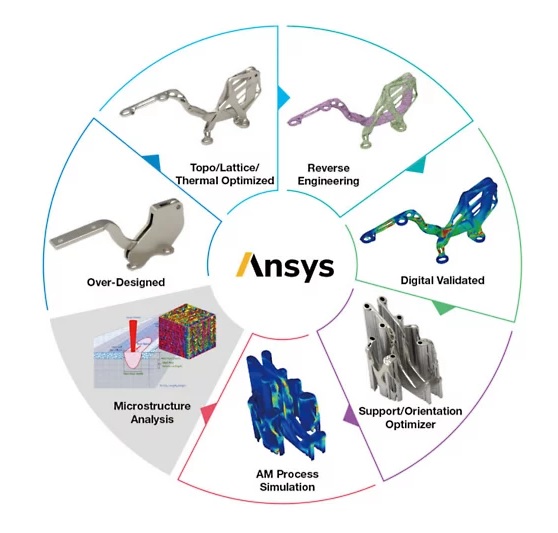
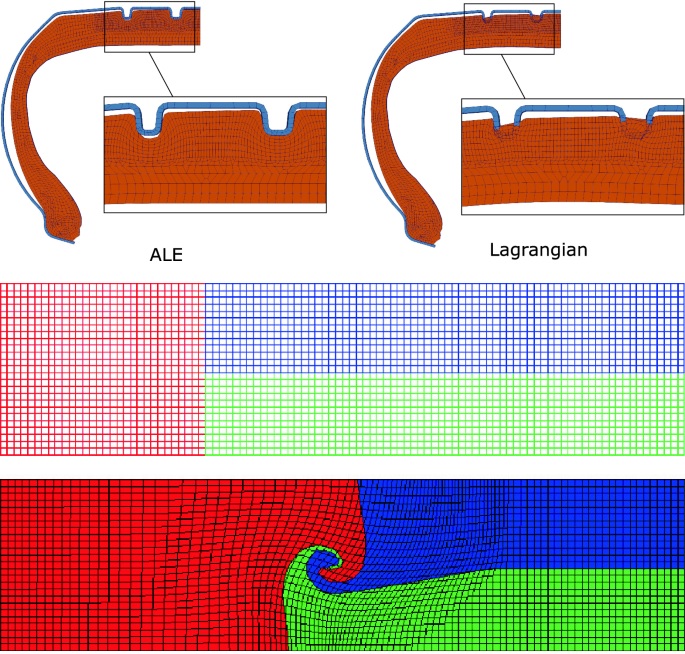
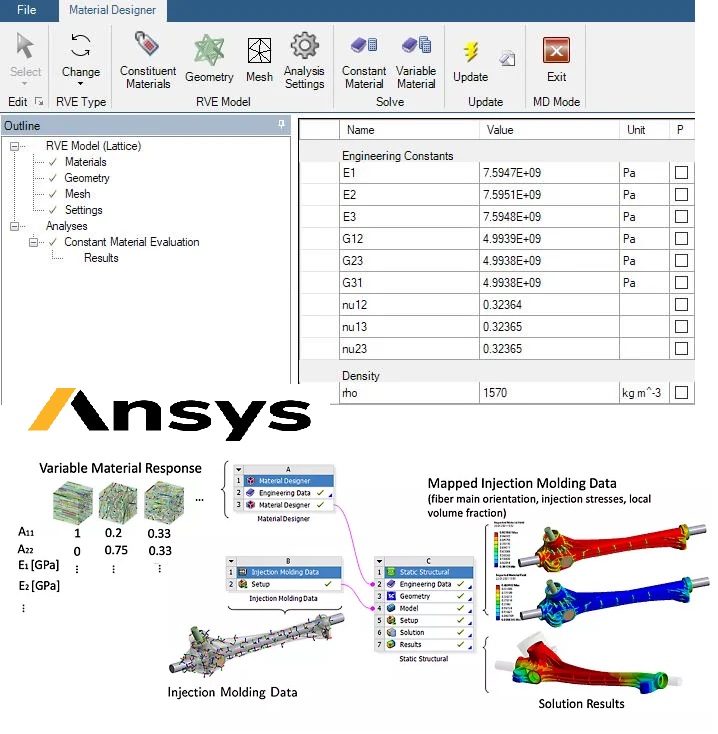
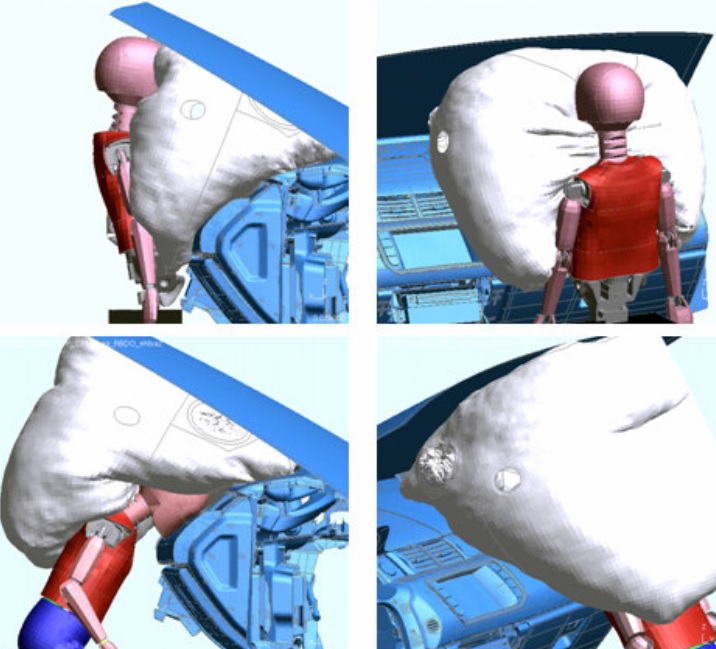
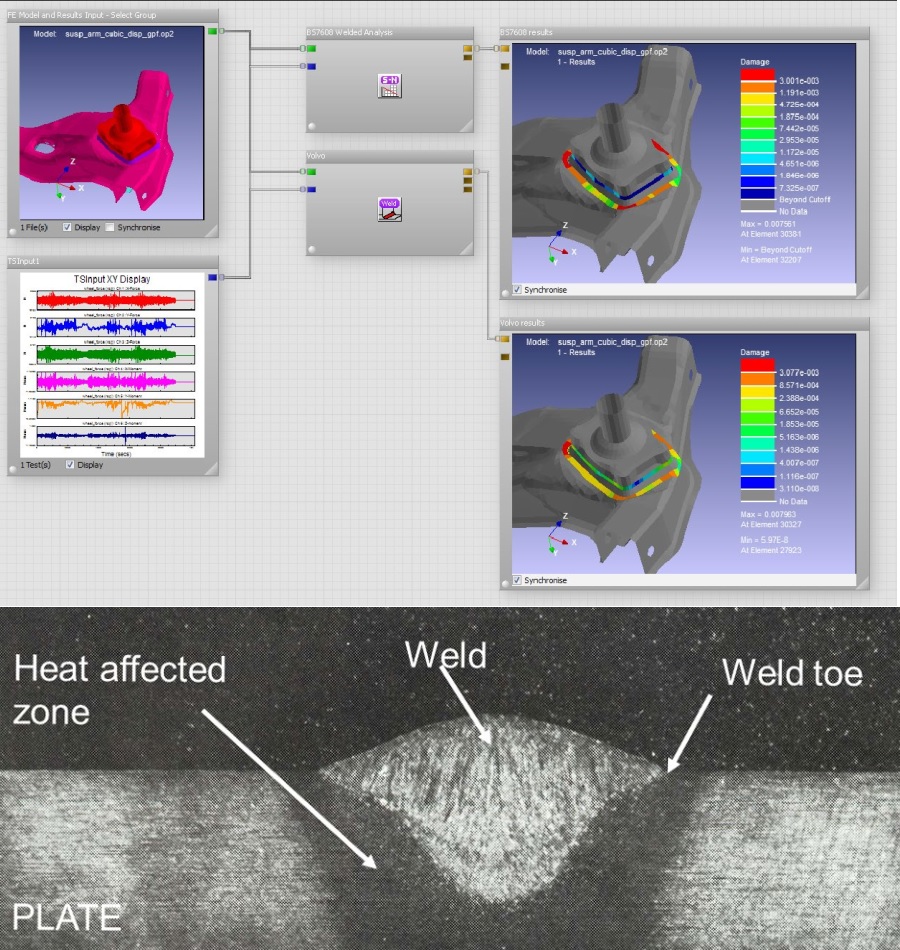
Pressure welding is a group of joining processes that use heat and pressure to join components together. These processes can be categorized into two main groups: resistance welding and friction welding.
Resistance welding involves passing an electrical current through the components being joined, which generates heat at the interface and melts the materials together. The two most common types of resistance welding are spot welding and seam welding. In spot welding, a small area of the components is heated and fused together, while in seam welding, a continuous seam is created along the length of the components.
Friction welding involves rubbing two components together at high speed to generate heat, which melts the materials and creates a bond between them. The two most common types of friction welding are rotary friction welding and linear friction welding. In rotary friction welding, one component is rotated against another component until they heat up and bond together. In linear friction welding, the components are moved back and forth against each other until they bond together.